Abstract
Background
A major destructive earthquake is predicted to shake the Tehran city in the near future. To mitigate the damage from such earthquakes, it is necessary to assess the preparedness of people and find the related risk factors.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted in Tehran city among people aged 15 years or older in 2009. 1195 of Tehran’s residents were interviewed using a questionnaire. Pearson chi-square test and binary logistic regression were used in order to evaluate the factors associated with preparedness against an earthquake.
Results
The analysis showed that 1076 (90.0%), 1160 (97.1%), and 490 (41.0%) of the participants achieved half of the possible scores for the knowledge, attitude, and practice components, respectively. Furthermore, in multivariate analysis low knowledge (p<0.001), having a high-school (p=0.033) or lower education (p<0.001) and living in Northern high-risk regions (p<0.001) of the Tehran were identified as risk factors for taking precautionary measures against earthquake. For low knowledge, lack of previous experience (p<0.001), and working as labor, businessman, employee (p=0.001) or being housewife (p=0.002) were related risk factors. In addition, people in the Southern high risk regions were significantly more knowledgeable (OR=0.618 compared to people in low risk regions) about earthquakes.
Conclusions
It is suggested that preparedness programs should target people with lower educational level and people in high risk regions especially the Northern districts of the city and aim at increasing public knowledge about earthquakes.
Address for correspondence: Ali Ardalan, No. 78, Italia Ave, Department of Disaster Public Health, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Email: [email protected] or [email protected]
Citation: Ostad Taghizadeh A, Hosseini M, Navidi I, Mahaki AA, Ammari H, Ardalan A. Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Tehran’s Inhabitants for an Earthquake and Related Determinants. PLOS Currents Disasters. 2012 Aug 6
Funding Statement
This project was supported by Social and Cultural Studies Department of Tehran Municipality.Introduction
Based on the observations since 1900, one earthquake of magnitude 8 or greater, 15 earthquakes of magnitude 7-7.9 and 134 earthquakes of magnitude 6-6.9 on the Richter scale are expected each year, worldwide.1 The number of large earthquakes has remained relatively constant, however, due to the increasing number of seismological stations, the observed number of smaller earthquakes (of magnitude lesser than 6) has increased each year.2 During the first decade of the 21st century, 4,022 natural disasters have been reported, 284 (7%) of which were earthquakes. Although they constitute a small share among the number of disasters, earthquakes are the major cause of death (55.7%) and cause US$232,070 million worth of damage (22%) comparing to other natural phenomena.3 Earthquakes have been the cause of 97.0% of deaths occurred as a result of natural hazards in Iran during the last four decades.
Tehran, the capital city and the most inhabited city of Iran, is located in a high seismic zone that is the result of its location in the main part of Alpine-Himalayan orogenic belt. The city has recorded many earthquakes during its history.4 Many studies have suggested that a large earthquake is expected to occur in the near-future.56 Historical data from 4 BC to 1830 AD show that eight large destructive earthquakes shook this region and caused severe damages to Shahre Ray, a part of Tehran at the present time. More recently, three notable earthquakes that occurred in this region are those of Buin Zahra (1962 ), Changureh (Avaj, 2002 ) and Firozabad Kojor (2004 ).7 The 1962 Buin Zahra earthquake resulted in 12,225 fatalities.8
The Bam earthquake was the latest major earthquake in Iran, this shook the Bam city and a large area of the Kerman province on December 26, 2003.9 More than 30,000 people were killed, 30,000 injured, about 75,000 became homeless and 85% of buildings damaged or destroyed.8 The Bam earthquake can be considered a turning point in the improvement of Iran’s disaster risk reduction efforts at national and local levels.10
This disaster made the Iranians more cautious about the same event in the capital city of Tehran, to an extent that the Iranian government considered moving the capital to another city11 to reduce the population of this region which is estimated to be more than 12 million.12
To mitigate the damage from the earthquakes, some precautionary actions can be taken, such as earthquake insurance or fixing high furniture securely; however, people in both developing and developed countries do not utilize these actions.13
The question “Why some people become prepared for natural hazards but not all?” or in other words “What motivates people to take precautionary actions in order to mitigate damage from the hazards?” has been addressed abundantly in the literature. The answers are varied depending on the type of hazard and the region studied. The findings show that the income and economic level1415 , educational level1516 , home ownership171819 and length of residence20 are factors associated with taking precautionary actions against various hazards in some regions. Some factors such as social class for flood preparedness are argued to be significant in some regions but not in others. The latest research which has some similarities in socioeconomic levels with Iran was conducted in Istanbul by Tekeli-Yeşil et al.16 Their findings suggested that educational level is the major factor associated with taking precautionary measures against an earthquake. Location of the home, participating in rescue actions after previous earthquakes, knowledge about earthquake, tenure, attitude score, age and general safety are other factors that were associated with taking precautionary measures against an earthquake.
Only a few researches have studied the factors associated with earthquake preparedness in Iran. As indicated above, the factors may vary between regions. The latest published research studied the factors using a KAP study with data from 2007.12 Their findings suggested that occupation, location of the home, age group and education are among the factors that can influence the knowledge, attitude and practice toward the earthquake preparedness.
After the Bam earthquake, the Iranian government has executed several preparedness programs. It is thus necessary to assess the efficiency of these programs and to identify the social groups that are in most need of related interventions. We also considered it necessary to reevaluate the population preparedness for earthquake and identify differences among different social groups. In addition, we aimed to estimate the associated factors using statistical methods.
Methods
Sample and Procedure. A cross-sectional survey conducted by the Social and Cultural Studies Department, Tehran Municipality employed a questionnaire of 80 questions. This study focused on 31 of those questions, which included the participants’ demographic characteristics, their knowledge about earthquakes and their attitude toward earthquakes and uptake of precautiounary measures.
The target population included residents of Tehran 15 years of age or older, staying in Tehran in the year of 2009. Initially, the sample size for the estimation of components of interest (Knowledge, Attitude and Practice regarding earthquake preparedness) was calculated using n=(z21-α/2×p×(1-p))/d2 with p=0.50 for each component considering α=0.05 and the precision of 3% (d=0.03) which yielded a total number of 1067 to be a reasonable for the aims of this study. However, using a random stratified-systematic sampling method, 1195 records were finally sampled.
First, in each of the 22 city’s districts, the number of samples were calculated proportionally to the size of the district’s population. Second, a block was chosen randomly in each district. Finally, trained interviewers started from the first unit of the block, filled the questionnaire for the household based on the responses from a person who was older than 15 years and capable to answer the questions. Then the interviewer systematically skipped next three units, interviewed the fifth household and continued until the end of the block. In the case that there were not enough samples in the block, interviewers filled the remaining questionnaires in the right hand side block.
Measurements
Demographic variables. Eight questions were asked by the interviewers to assess the demographic characteristics of the participants: age, sex, education, previous earthquake experience, home ownership, length of residence, marital status and occupation.
Region. Based on the district of each participant and the location of the faults which are showed in Fig. 1, the region of each participant was categorized into three groups: (I) Low risk regions: These districts are not on active seismic faults (districts #6,7,8,9,10,11,12,17,18). (II) Southern high-risk regions (districts #13,14,15,16,19,20) and (III) Northern high-risk regions (districts #1,2,3,4,5,21,22): The Southern and Northern districts of Tehran which were on active seismic faults. Distinguishing the Northern and Southern high-risk districts (regions) was due to different socio-economic characteristics of these regions. In addition, previous studies have shown that buildings in the Northern districts are less vulnerable to the earthquake than those in the Southern area.6
Source: Available online at https://abbasimehr.ir/blog/wp-content/uploads/2010/04/tehran_fault_map.jpg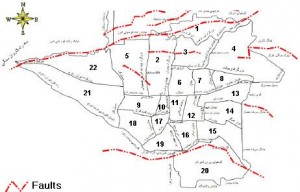
Fig. 1: Tehran Districts and Faults
Knowledge about earthquake preparedness. Ten questions were asked to evaluate the participants’ knowledge of safety measures during an earthquake. Each question asked about safe places during an earthquake. Participants got 1 score for each correct answer and 0 for an incorrect one . The sum of the scores was used as the knowledge score for each participant. The median of the score of all participants was calculated and any participant with a score lower than the median, was regarded as a participant with low knowledge.
Attitude toward earthquake preparedness. Three questions were asked to assess the attitude of the participants toward the earthquake. Questions like “Earthquakes can be avoided by praying” were in this section. A score from 1 through 5 was set to each question in which 1 stands for the lowest attitude and 5 for the highest. The sum of these three questions was assumed as the attitude score (Cronbach’s α=0.65). Any participant with an attitude score lower than median was regarded as participant with low attitude.
Taking precautionary actions (Practice component). Nine yes/no questions were asked by interviewers to evaluate the measure of precautionary actions for each participant. The questions were about the precautionary actions that can mitigate the damages of earthquakes such as “Does your house have an earthquake insurance?”. The sum of yes answers considered as the practice score (Cronbach’s α=0.74). The median for this score which considered as cut-off point was 3, thus any participant with practice score lower than 3 considered as participant with low practice.
Analysis. SPSS 11.5 have been used in order to record and analyze the data. All demographic variables were assumed as categorical variables. To avoid the effect of missing values, for each of knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) components, the summation based on the mean of answered questions was assumed as the score. For example if three questions out of ten of the knowledge component were missing, the mean of the seven remained questions multiplied by 10 assigned as the score of knowledge for that observation.
The score of the KAP components were analyzed and median used as the cut off point for categorizing these components, such that if an observation’s knowledge score was bellow the median, that observation was considered as having low knowledge. The same applied to the attitude and practice components and three new binary variables extracted.
We used frequency tables to present the characteristics of study population. As the “other” group in the marital status category and the “military” group in the occupation category had a small number of observations, we removed them from further analysis in this study. Cross-tabulation was used in order to present the distribution of the answers based on the factor variables for each component and chi-square test applied to test whether the components and demographic variable were independent or not. Instead of chi-square p-value, the p-value of Fisher Exact test is reported wherever it was possible to use this test.
To assess the relationship of demographic factors and KAP components by adjusting other factors, multiple binary logistic regression was used. For each regression model, the significance level and odd ratio and its 95% confidence interval are reported. Factors which were significant (at α≤0.2 level) at previous univariate tests entered in the regression model and the forward likelihood ratio method was used to dismiss the effect of non-significant factors. As low knowledge and attitude toward earthquake were significant factors for practice components, we entered these two component as well as other significant factors into the regression model for low practice. P-value < 0.05 was supposed as significant for all logistic regressions and 0.05 assigned as entry probability for the stepwise method.
Results
Between June and October 2009, 1195 Tehran’s residents were interviewed in Tehran, Iran. The characteristics of the study population are shown in Table I. Of the participants, 717 (60.1%) were aged 21-45 years old and the ratio of male to female was nearly 1. In addition, 322 (27.0%) had received education lower than high school or were or illiterate and about 30% of the participants were single. Furthermore, 959 (79.9%) of the participants had faced an earthquake at least once in the past and 1014 (90.9%) of them had been living in Tehran for more than ten years. Besides, 1076 (90.0%), 1160 (97.1%), and 490 (41.0%) achieved half of the possible scores for knowledge, attitude and practice components, respectively.
| Variable | Group | Frequency* | Percent† |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group | |||
| 15-12 | 133 | 11.1% | |
| 21-45 | 717 | 60.1% | |
| 46-65 | 266 | 22.3% | |
| >65 | 78 | 6.5% | |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 623 | 52.1% | |
| Female | 572 | 47.9% | |
| Educational level | |||
| Illiterate | 55 | 4.6% | |
| Under high school | 267 | 22.4% | |
| High school | 516 | 43.3% | |
| Higher educations | 353 | 29.6% | |
| Earthquake experience | |||
| Yes | 949 | 79.9% | |
| No | 238 | 20.1% | |
| Home ownership | |||
| Owner | 808 | 68.7% | |
| Tenure | 368 | 31.3% | |
| Length of residence | |||
| Less than 3 years | 35 | 3.1% | |
| 3 to 10 years | 66 | 5.9% | |
| More than 10 years | 1014 | 90.9% | |
| Region | |||
| Low risk region | 438 | 36.7% | |
| Southern high risk region | 335 | 28.0% | |
| Northern high risk region | 422 | 35.3% | |
| Marital status | |||
| Single | 353 | 36.7% | |
| Married | 819 | 28.0% | |
| Other | 16 | 35.3% | |
| Occupation | |||
| Labor, businessman, or employee | 418 | 35.3% | |
| Student | 238 | 20.1% | |
| Housewife | 379 | 32.0% | |
| Jobless | 47 | 4.0% | |
| Military | 6 | 0.5% | |
| Retired | 97 | 8.2% |
Table II displays the results of univariate analysis of the factors affecting KAP components as well as the association between knowledge and attitude components with practice.
Results from Table II show that low knowledge about earthquake was significantly associated with higher age groups and lack of previous earthquake experience, and had a significant association with the occupation and region of the participant. Lower attitude was significantly associated with increasing age, length of residence and being married. The attitude component also had a significant negative association with educational level and was associated with sex, region and occupation of the participant. Furthermore, there was a significant association between the practice component and previous earthquake experience, region of the participant, low knowledge about earthquake and low attitude toward earthquake, and there was a significant negative relation between educational level and practice component. It should be noted that this results are tested independently; it means that the associations found here might be confounded by the effect of other factors.
* Fisher exact test
Factor
Group
Low knowledge
Low attitude
Low Practice
n (%)
p-value
n (%)
p-value
n (%)
p-value
Age group
0.036
<0.001
0.336
15-20
40 (30.3%)
81 (61.4%)
59 (44.4%)
21-45
312 (43.6%)
358 (50.2%)
318 (44.4%)
46-65
114 (43.5%)
185 (72.5%)
123 (46.2%)
>65
34 (44.2%)
58 (76.3%)
43 (55.1%)
Sex*
0.557
0.018
0.245
Male
267 (43.0%)
334 (54.7%)
273 (43.9%)
Female
234 (41.3%)
348 (61.5%)
271 (47.4%)
Educational level
0.171
<0.001
<0.001
Illiterate
26 (48.1%)
43 (81.1%)
39 (70.9%)
Under high school
124 (46.4%)
171 (66.3%)
152 (56.0%)
High school
215 (42.2%)
312 (61.1%)
223 (43.3%)
Higher educations
135 (38.2%)
154 (43.9%)
128 (36.3%)
Marital status*
0.561
<0.001
0.201
Single
142 (40.5%)
171 (49.0%)
149 (42.2%)
Married
345 (42.4%)
496 (61.5%)
380 (46.5%)
Occupation
0.040
0.001
0.108
Labor, businessman, or employee
190 (45.6%)
217 (52.8%)
180 (43.2%)
Student
79 (33.3%)
122 (51.5%)
96 (40.3%)
Housewife
165 (43.9%)
246 (65.8%)
189 (49.9%)
Jobless
20 (42.6%)
27 (57.4%)
23 (48.9%)
Retired
41 (43.2%)
60 (65.2%)
49 (50.5%)
Home ownership*
0.949
0.277
0.487
Owner
340 (42.3%)
468 (59.1%)
374 (46.3%)
Tenure
154 (42.1%)
204 (55.6%)
162 (44.0%)
Earthquake experience*
<0.001
>0.999
0.019
Yes
363 (38.5%)
546 (58.0%)
414 (43.6%)
No
132 (55.5%)
133 (58.1%)
124 (52.3%)
Length of residence
0.933
0.028
0.231
Less than 3 years
13 (37.1%)
14 (40.0%)
20 (57.1%)
3 to 10 years
27 (40.9%)
36 (54.5%)
26 (39.4%)
More than 10 years
402 (39.9%)
610 (61.1%)
454 (44.8%)
Region
0.004
0.006
0.011
Low risk region
204 (46.9%)
254 (58.7%)
178 (40.7%)
Southern high risk region
117 (35.0%)
210 (64.0%)
151 (45.1%)
Northern high risk region
180 (43.0%)
218 (52.4%)
215 (50.9%)
Low knowledge*
–
–
<0.001
Yes
–
–
281 (56.1%)
No
–
–
259 (37.8%)
Low attitude*
–
–
0.033
Yes
–
–
325 (47.7%)
No
–
–
205 (41.4%)
In order to adjust for the effect of possible confounders, a multiple binary logistic regression method was used. Table III shows the result of logistic regression of knowledge component on factors using forward method. The result of this analysis shows that lack of previous earthquake experience, region and occupation of the participants remained as significant predictors for low knowledge.
† Only the factors that were significant in the last step are reported here * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001
Factor†
Group
OR
95% CI
Earthquake experience
Yes
1
No**
1.980
1.471
2.665
Region
Low risk region
1
Southern high risk region*
0.618
0.456
0.836
Northern high risk region
0.864
0.655
1.141
Occupation
Student
1
Labor, businessman, or employee*
1.786
1.272
2.507
Housewife*
1.732
1.223
2.451
Jobless
1.773
0.925
3.399
Retired
1.617
0.985
2.655
Older age and lower educational level remained as risk factors on low attitude toward earthquake (Table IV). In addition, low practice was significantly linked to lower levels of education, low knowledge and region of the participants when educational level, previous earthquake experience, region of the participant, low knowledge and low attitude were entered in a multivariate logistic regression, as shown in Table V.
† Only the factors that were significant in the last step are reported here * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001
Factor†
Group
OR
95% CI
Age group
21-45
1
15-20
1.313
0.883
1.953
45-65**
2.233
1.608
3.100
> 65*
2.252
1.256
4.039
Educational level
Higher education
1
Illiterate*
3.363
1.573
7.188
Under high school**
1.926
1.352
2.742
High school**
1.806
1.352
2.411
† Only the factors that were significant in the last step are reported here * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.001
Factor†
Group
OR
95% CI
Educational level
Higher education
1
Illiterate**
4.825
2.517
9.251
Under high school**
2.422
1.721
3.408
High school*
1.365
1.025
1.819
Low knowledge
No
1
Yes**
2.110
1.656
2.688
Region
Low risk region
1
Southern high risk region
1.147
0.845
1.558
Northern high risk region**
1.711
1.289
2.271
Discussion
Our findings showed that people with a lower educational level are at higher risk of unpreparedness than people with a higher education. People in the Northern high-risk regions are less prepared than people in low-risk regions. The analysis also showed that low knowledge can cause low preparedness. Low knowledge, however, is affected by previous earthquake experience, the region and occupation by itself. Furthermore, the attitude component was also affected by the educational level and age group.
In the latest study conducted in Tehran12 , age, occupation and location of the participants were suggested to be associated with low preparedness. Although our results showed higher risk for older people, the difference was not significant in both univariate and multivariate analysis. Occupation had the same results in our study. Also, our study showed a significant difference in region groups which is similar to the study by Jahangiri et al. Our study showed that people in high-risk regions are less prepared than people in low risk regions. The reason for this might be the reliance of people in Northern vulnerable regions on their secure buildings21 or cultural aspects related to higher socio-economic class or less attention to the media.
In our study, the attitude toward earthquake was not a significant factor for taking precautionary actions against an earthquake after multivariate analysis, however, Tekeli‐Yeşil et al.16 showed that it was a significant factor together with education, location of the home, knowledge, previous earthquake experience, home ownership, age and general safety in Istanbul, Turkey. Our analysis showed that attitude and knowledge about an earthquake are significantly related to each other. As the relationship between knowledge and the practice component was also significant in our study, this might have resulted in the removal of attitude from the multivariate analysis.
As in other cities around the world, different regions of Tehran have different socio-economic characteristics . If we consider the region in our study as a socio-economic factor, our findings replicate the effect of economic level and social classes on the practice component which was shown in the USA14, Turkey15 , and Iran22 . However, our analysis did not show any significant association between home ownership and practice which was on the other hand reported in New Zealand19 and Turkey16,nor length of residence as shown in a study from the USA.20
Although we tried to assess the effect of all the factors used by previous studies, we did not have data on some of them, such as the risk perception which was employed previously.1622 Spittal et al. have distinguished the survival and mitigate types of preparedness 19 , however, in our study, the practice component was a combination of these two. Although we distinguished the Southern and Northern high-risk regions to check the effect of secure and insecure buildings, it is suggested to use building type as an independent factor for future research.
Conclusions
Our findings show that general education, region and knowledge about earthquakes are the factors which can influence the behavior of Tehran residents during an earthquake. Therefore, in order to mitigate the damage from future earthquakes, it will be importnat to increase the population’s general education as well as their knowledge about earthquakes, especially for those in high-risk regions.
References
- USGS Earthquake Facts and Statistics. Available at:https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqarchives/year/eqstats.php. Accessed on December 15, 2011.
Reference Link - USGS Are Earthquakes Really on the Increase? Available at:https://earthquake.usgs.gov/learn/topics/increase_in_earthquakes.php. Accessed on December 15, 2011.
Reference Link - International Federation of Red Cross. World Disaster Report. IFRC, Switzerland. 112-123 pp., 2011
Reference Link - Zafarani H, Noorzad A, Ansari A, Bargi K. Stochastic modeling of Iranian earthquakes and estimation of ground motion for future earthquakes in Greater Tehran.Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2009; 29(4): 722-741
- Ashtari Jafari M. Statistical prediction of the next great earthquake around Tehran, Iran.Journal of Geodynamics, 2010; 49(1): 14-18
- Amini Hosseini K, Hosseini M, Jafari M, Hosseinioo S. Recognition of Vulnerable Urban Fabrics in Earthquake Zones: A Case Study of the Tehran Metropolitan Area.Journal of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, 2011; 10(4): 175-187
- Hamzehloo H, Sinaeian F, Mahood M, Mirzaei Alavijeh H, Farzanegan E. Determination of Causative Fault Parameters for the October 17, 2009, Ray-Tehran Earthquake, Using Near Field SH-Wave Data.Journal of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering, 2009; 11(3): 121-131
- United States Geographical Survey. Earthquakes with 1,000 or More Deaths since 1900. Available at:https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/world/world_deaths.php. Accessed on December 15, 2011
Reference Link - United States Geographical Survey. Magnitude 6.6 - SOUTHEASTERN IRAN. Available at:https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eqinthenews/2003/uscvad/. Accessed on December 15, 2011
Reference Link - Ardalan A, Masoomi GR, Goya M, Ghaffari M, Miadfar J, Sarvar MR, Soroush M, Maghsoodi A, Holakouie Naieni K, Kabir MJ, Khankeh HR, Abolshams B, Aghazadeh M. Disaster Health Management: Iran’s Progress and Challenges. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 2009; 38 Suppl 1:93-7
- Tamaddon N. Iran moots shifting capital from Tehran. The Messenger, 2010; 132: 7-7
- Jahangiri K, Azin S, Mohammad K, Rahimi Foroushani A. Factors affecting Tehran’s residents’ preparedness against earthquake in 2007. HAKIM, 2010; 13(3): 155-164
- Tekeli-Yeşil S, Dedeoğlu N, Braun-Fahrlaender C, Tanner M. Earthquake awareness and perception of risk among the residents of Istanbul. Natural hazards, 2011; 59: 1-20
- Russell LA, Goltz JD, Bourque LB. Preparedness and hazard mitigation actions before and after two earthquakes. Environment and Behavior, 1995; 27(6): 744-770
- Dedeoglu N. (2006). Knowledge, attitude and practice of residents of Antalya, Turkey about earthquake preparedness. International Disaster Reduction Conference, Davos, Switzerland
- Tekeli‐Yeşil S, Dedeoğlu N, Braun‐Fahrlaender C, Tanner M. Factors Motivating Individuals to Take Precautionary Action for an Expected Earthquake in Istanbul.Risk Analysis, 2010; 30(8): 1181-1195
- Mullis JP, Duval TS, Bovalino K. Tornado Preparedness of Students, Nonstudent Renters, and Nonstudent Owners: Issues of PrE Theory1. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 2000; 30(6): 1310-1329
- Heller K, Alexander DB, Gatz M, Knight BG, Rose T. Social and Personal Factors as Predictors of Earthquake Preparation: The Role of Support Provision, Network Discussion, Negative Affect, Age, and Education1. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 2005; 35(2): 399-422
- Spittal MJ, McClure J, Siegert RJ, Walkey FH. Predictors of two types of earthquake preparation. Environment and Behavior, 2008; 40(6): 798-817
- Duval TS, Mulilis JP. A Person‐Relative‐to‐Event (PrE) Approach to Negative Threat Appeals and Earthquake Preparedness: A Field Study1. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 1999; 29(3): 495-516
- Zangi Abadi A, Tabrizi N. Tehran earthquake and assessment of the vulnerability of urban districts. Geographical researches, 2006; 38(56): 115-130
- Asgary A, Willis K. Household behaviour in response to earthquake risk: An assessment of alternative theories. Disasters, 1997; 21(4): 354-365

Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.