The wars in the Middle East have led to unprecedented threats and attacks on patients, healthcare workers, and purposeful targeting of hospitals and medical facilities. It is crucial that every healthcare provider, both civilian and military, on either side of the conflict become aware of the unique and inherent protections afforded to them under International Humanitarian Law. However, these protections come with obligations. Whereas Governments must guarantee these protections, when violated, medical providers have equal duty and obligations under the Law to ensure that they will neither commit nor assist in these violations nor take part in any act of hostility. Healthcare providers must not allow any inhuman or degrading treatment of which they are aware and must report such actions to the appropriate authorities. Failure to do so leads to risks of moral, ethical and legal consequences as well as penalties for their actions and inactions. There must be immediate recognition by all parties of the neutrality of health care workers and their rights and responsibilities to care for any sick and injured patient, regardless of their nationality, race, religion, or political point of view.
Author Profile
Recent Posts
An increasing number of international emergency medical teams are deployed to assist disaster-affected populations worldwide. Since Haiti earthquake those teams have been criticised for ill adapted care, lack of preparedness in addition to not coordinating with the affected country healthcare system. The Emergency Medical Teams (EMTs) initiative, as part of the Word Health Organization’s Global Health Emergency Workforce program, aims to address these shortcomings by improved EMT coordination, and mechanisms to ensure quality and accountability of national and international EMTs. An essential component to reach this goal is appropriate education and training. Multiple disaster education and training programs are available. However, most are centred on individuals’ professional development rather than on the EMTs operational performance. Moreover, no common overarching or standardised training frameworks exist. In this report, an expert panel review and discuss the current approaches to disaster education and training and propose a three-step operational learning framework that could be used for EMTs globally. The proposed framework includes the following steps: 1) ensure professional competence and license to practice, 2) support adaptation of technical and non-technical professional capacities into the low-resource and emergency context and 3) prepare for an effective team performance in the field. A combination of training methodologies is also recommended, including individual theory based education, immersive simulations and team training. Agreed curriculum and open access training materials for EMTs need to be further developed, ideally through collaborative efforts between WHO, operational EMT organizations, universities, professional bodies and training agencies. Keywords: disasters; education; emergencies; global health; learning
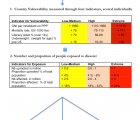
Background: Humanitarian assistance is designated to save lives and alleviate suffering among people affected by disasters. In 2014, close to 25 billion USD was allocated to humanitarian assistance, more than 80% of it from governmental donors and EU institutions. Most of these funds are devoted to Complex Emergencies (CE). It is widely accepted that the needs of the affected population should be the main determinant for resource allocations of humanitarian funding. However, to date no common, systematic, and transparent system for needs-based allocations exists. In an earlier paper, an easy-to-use model, “the 7eed model”, based on readily available indicators that distinguished between levels of severity among disaster-affected countries was presented. The aim of this paper is to assess the usefulness of the 7eed model in regards to 1) data availability, 2) variations between CE effected countries and sensitivity to change over time, and 3) reliability in capturing severity and levels of need.
Method: We applied the 7eed model to 25 countries with CE using data from 2013 to 2015. Data availability and indicator value variations were assessed using heat maps. To calculate a severity score and a needs score, we applied a standardised mathematical formula, based on the UTSTEIN template. We assessed the model for reliability on previous CEs with a “known” outcome in terms of excess mortality.
Results: Most of the required data was available for nearly all countries and indicators, and availability increased over time. The 7eed model was able to discriminate between levels of severity and needs among countries. Comparison with historical complex disasters showed a correlation between excess mortality and severity score.
Conclusion: Our study indicates that the proposed 7eed model can serve as a useful tool for setting funding levels for humanitarian assistance according to measurable levels of need. The 7eed model provides national level information but does not take into account local variations or specific contextual factors.
Background: Disasters affect close to 400 million people each year. Complex Emergencies (CE) are a category of disaster that affects nearly half of the 400 million and often last for several years. To support the people affected by CE, humanitarian assistance is provided with the aim of saving lives and alleviating suffering. It is widely agreed that funding for this assistance should be needs-based. However, to date, there is no model or set of indicators that quantify and compare needs from one CE to another. In an effort to support needs-based and transparent funding of humanitarian assistance, the aim of this study is to develop a model that distinguishes between levels of severity among countries affected by CE.
Methods: In this study, severity serves as a predictor for level of need. The study focuses on two components of severity: vulnerability and exposure. In a literature and Internet search we identified indicators that characterize vulnerability and exposure to CE. Among the more than 100 indicators identified, a core set of six was selected in an expert ratings exercise. Selection was made based on indicator availability and their ability to characterize preexisting or underlying vulnerabilities (four indicators) or to quantify exposure to a CE (two indicators). CE from 50 countries were then scored using a 3-tiered score (Low-Moderate, High, Critical).
Results: The developed model builds on the logic of the Utstein template. It scores severity based on the readily available value of four vulnerability and four exposure indicators. These are 1) GNI per capita, PPP, 2) Under-five mortality rate, per 1 000 live births, 3) Adult literacy rate, % of people ages 15 and above, 4) Underweight, % of population under 5 years, and 5) number of persons and proportion of population affected, and 6) number of uprooted persons and proportion of population uprooted.
Conclusion: The model can be used to derive support for transparent, needs-based funding of humanitarian assistance. Further research is needed to determine its validity, the robustness of indicators and to what extent levels of scoring relate to CE outcome.
Background: Foreign medical teams (FMT) are international medical teams sent to provide assistance in the aftermath of a disaster. In the last decade, there has been an increase in FMTs deployed following disasters. Despite the potential benefit FMTs might have in substituting the collapsed health care and caring for excess morbidity after large-scale disasters, several studies have demonstrated the difficulties in determining the quality of the response, mainly due to lack of reliable data. In order to bridge the knowledge gap on functioning of FMTs, the aim of this study is to assess the timing, capacities and activities of FMTs deployed to the Philippines after typhoon Haiyan.
Methods: This is a retrospective, descriptive study. Data on characteristics of FMTs present in the Philippines after typhoon Haiyan was provided by the World Health Organization (WHO) and compiled into a single database. Additional data was collected through a web survey, email correspondence and internet searches.
Results: A total of 108 FMTs were identified as arriving to the Philippines within the first month following typhoon Haiyan. None of these were operational in the affected areas within the first 72 h and the average time between arriving and being on-site operational was three days. Of the 108 FMTs, 70% were FMT type 1, 11% were FMT type 2 and 3% were FMT type 3. 16% of FMTs had unknown status. The total number of staff within all these FMTs were 2121, of which 210 were medical doctors, 250 nurses and 6 midwifes. Compared to previous sudden onset disasters, this study found no improvement in data sharing.
Background: International humanitarian assistance is essential for disaster-affected populations, particularly in resource scarce settings. To target such assistance, needs assessments are required. According to internationally endorsed principles, donor governments should provide funding for humanitarian assistance based on need.
Aim: The aim of this study is to explore a major donor’s use of needs assessment data in decision-making for allocations of funds for health-related humanitarian assistance contributions.
Setting: This is a case study of the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida), a major and respected international donor of humanitarian assistance.
Methods: To explore Sida’s use of needs assessment data in practice for needs-based allocations, we reviewed all decision documents and assessment memoranda for humanitarian assistance contributions for 2012 using content analysis; this was followed by interviews with key personnel at Sida.
Results: Our document analysis found that needs assessment data was not systematically included in Sida’s assessment memoranda and decision documents. In the interviews, we observed various descriptions of the concept of needs assessments, the importance of contextual influences as well as previous collaborations with implementing humanitarian assistance organizations. Our findings indicate that policies guiding funding decisions on humanitarian assistance need to be matched with available needs assessment data and that terminologies and concepts have to be clearly defined.
Conclusion: Based on the document analysis and the interviews, it is unclear how well Sida used needs assessment data for decisions to allocate funds. However, although our observations show that needs assessments are seldom used in decision making, Sida’s use of needs assessments has improved compared to a previous study. To improve project funds allocations based on needs assessment data, it will be critical to develop distinct frameworks for allocation distributions based on needs assessment and clear definitions, measurements and interpretations of needs.
Key words: Needs assessment, humanitarian assistance, disasters, donor decision-making
Background
To adequately plan relief, adequate information that describe and quantify the severity of a disaster, and estimate the number of affected population, is rapidly needed. However, needs assessments describing the severity of the disaster has been shown to be conducted too late in order to guide the first days relief interventions. The aim of this study was to assess availability of early disaster severity information on Internet during the first seven days following the 2010 Haiti earthquake and assess to which extent the information was consistent with later revelations.
Methods
We searched the well acknowledged web portal Relief Web for all Haiti postings during the first seven days (12 -18 January 2010) after the earthquake. A form was created to classify and quantify extracted severity variables found in the postings. The results were compiled, analysed and compared with CRED (Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disaster) official data made available later.
Findings
A total of 822 reports were posted where of 15 % provided a numerical estimate of the affected population, while 10% had an estimate on the number of dead. On day four 200 000 dead was reported, which is of the same magnitud compared to later official estimates (CRED data). Not a single report described the data collection method.
Conclusions
Within a few days of the 2010 Haiti earthquake it was possible to find surprisingly accurate information regarding severity of the earthquake but the available data must be questioned as no method was reported. More specialized and independent needs assessment agencies may improve availability of strategic information in the early onset of a disaster.
