Introduction: Although many studies have investigated the probability of Ebola virus disease (EVD) outbreaks while other studies have simulated the size and speed of EVD outbreaks, few have investigated the environmental and population-level predictors of Ebola transmission once an outbreak is underway. Identifying strong predictors of transmission could help guide and target limited public health resources during an EVD outbreak. We examined several environmental and population-level demographic predictors of EVD risk from the West African epidemic. Methods: We obtained district-level estimates from the World Health Organization EVD case data, demographic indicators obtained from the Demographic and Health surveys, and satellite-derived temperature, rainfall, and land cover estimates. A Bayesian hierarchical Poisson model was used to estimate EVD risk and to evaluate the spatial variability explained by the selected predictors. Results: We found that districts had greater risk of EVD with increasing proportion of households not possessing a radio (RR 2.79, 0.90-8.78; RR 4.23, 1.16-15.93), increasing rainfall (RR 2.18; 0.66-7.20; 5.34, 1.20-23.90), and urban land cover (RR 4.87, 1.56-15.40; RR 5.74, 1.68-19.67). Discussion: The finding of radio ownership and reduced EVD transmission risk suggests that the use of radio messaging for control and prevention purposes may have been crucial in reducing the EVD transmission risk in certain districts, although this association requires further study. Future research should examine the etiologic relationships between the identified risk factors and human-to-human transmission of EVD with a focus on factors related to population mobility and healthcare accessibility, which are critical features of epidemic propagation and control.
Author Profile
Recent Posts
Introduction: Data from social media have been shown to have utility in augmenting traditional approaches to public health surveillance. Quantifying the representativeness of these data is needed for making accurate public health inferences.
Methods: We applied machine-learning methods to explore spatial and temporal dengue event reporting trends on Twitter relative to confirmed cases, and quantified associations with sociodemographic factors across three Brazilian states (São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais) at the municipality level.
Results: Education and income were positive predictors of dengue reporting on Twitter. In contrast, municipalities with a higher percentage of older adults, and males were less likely to report suspected dengue disease on Twitter. Overall, municipalities with dengue disease tweets had higher mean per capita income and lower proportion of individuals with no primary school education.
Conclusions: These observations highlight the need to understand population representation across locations, age, and racial/ethnic backgrounds in studies using social media data for public health research. Additional data is needed to assess and compare data representativeness across regions in Brazil.
Participatory systems for surveillance of acute respiratory infection give real-time information about infections circulating in the community, yet to-date are limited to self-reported syndromic information only and lacking methods of linking symptom reports to infection types. We developed the GoViral platform to evaluate whether a cohort of lay volunteers could, and would find it useful to, contribute self-reported symptoms online and to compare specimen types for self-collected diagnostic information of sufficient quality for respiratory infection surveillance. Volunteers were recruited, given a kit (collection materials and customized instructions), instructed to report their symptoms weekly, and when sick with cold or flu-like symptoms, requested to collect specimens (saliva and nasal swab). We compared specimen types for respiratory virus detection sensitivity (via polymerase-chain-reaction) and ease of collection. Participants were surveyed to determine receptivity to participating when sick, to receiving information on the type of pathogen causing their infection and types circulating near them. Between December 1 2013 and March 1 2014, 295 participants enrolled in the study and received a kit. Of those who reported symptoms, half (71) collected and sent specimens for analysis. Participants submitted kits on average 2.30 days (95 CI: 1.65 to 2.96) after symptoms began. We found good concordance between nasal and saliva specimens for multiple pathogens, with few discrepancies. Individuals report that saliva collection is easiest and report that receiving information about what pathogen they, and those near them, have is valued and can shape public health behaviors. Community-submitted specimens can be used for the detection of acute respiratory infection with individuals showing receptivity for participating and interest in a real-time picture of respiratory pathogens near them.
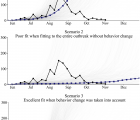
The West Africa Ebola virus epidemic now appears to be coming to an end. In the proposed model, we simulate changes in population behavior that help to explain the observed transmission dynamics. We introduce an EVD transmission model accompanied by a model of social mobilization. The model was fit to Lofa County, Liberia through October 2014, using weekly counts of new cases reported by the US CDC. In simulation studies, we analyze the dynamics of the disease transmission with and without population behavior change, given the availability of beds in Ebola treatment units (ETUs) estimated from observed data. Only the model scenario that included individuals’ behavioral change achieved a good fit to the observed case counts. Although the capacity of the Lofa County ETUs greatly increased in mid-August, our simulations show that the expansion was insufficient to alone control the outbreak. Modeling the entire outbreak without considering behavior change fit the data poorly, and extrapolating from early data without taking behavioral changes into account led to a prediction of exponential outbreak growth, contrary to the observed decline. Education and awareness-induced behavior change in the population was instrumental in curtailing the Ebola outbreak in Lofa County and is likely playing an important role in stopping the West Africa epidemic altogether.
In this commentary, we consider the relationship between early outbreak changes in the observed reproductive number of Ebola in West Africa and various media reported interventions and aggravating events. We find that media reports of interventions that provided education, minimized contact, or strengthened healthcare were typically followed by sustained transmission reductions in both Sierra Leone and Liberia. Meanwhile, media reports of aggravating events generally preceded temporary transmission increases in both countries. Given these preliminary findings, we conclude that media reported events could potentially be incorporated into future epidemic modeling efforts to improve mid-outbreak case projections.
Background: Global outbreak detection and reporting have generally improved for a variety of infectious diseases and geographic regions in recent decades. Nevertheless, lags in outbreak reporting remain a threat to the global human health and economy. In the time between first occurrence of a novel disease incident and public notification of an outbreak, infected individuals have a greater possibility of traveling and spreading the pathogen to other nations. Shortening outbreak reporting lags has the potential to improve global health by preventing local outbreaks from escalating into global epidemics.
Methods: Reporting lags between the first record and the first public report of an event were calculated for 318 outbreaks occurring 1996-2009. The influence of freedom of the press, Internet usage, per capita health expenditure, and cell phone subscriptions, on the timeliness of outbreak reporting was evaluated.
Results: Freer presses and increasing Internet usage correlate with reduced time between the first record of an outbreak and the public report. Increasing Internet usage reduced the expected reporting lag from more than one month in nations without Internet users to one day in those where 75 of 100 people use the Internet.
Conclusion: Advances in technology and the emergence of more open and free governments are associated with to improved global infectious disease surveillance.
Background: For the first time, an outbreak of chikungunya has been reported in the Americas. Locally acquired infections have been confirmed in fourteen Caribbean countries and dependent territories, Guyana and French Guiana, in which a large number of North American travelers vacation. Should some travelers become infected with chikungunya virus, they could potentially introduce it into the United States, where there are competent Aedes mosquito vectors, with the possibility of local transmission.
Methods: We analyzed historical data on airline travelers departing areas of the Caribbean and South America, where locally acquired cases of chikungunya have been confirmed as of May 12th, 2014. The final destinations of travelers departing these areas between May and July 2012 were determined and overlaid on maps of the reported distribution of Aedes aeygpti and albopictus mosquitoes in the United States, to identify potential areas at risk of autochthonous transmission.
Results: The United States alone accounted for 52.1% of the final destinations of all international travelers departing chikungunya indigenous areas of the Caribbean between May and July 2012. Cities in the United States with the highest volume of air travelers were New York City, Miami and San Juan (Puerto Rico). Miami and San Juan were high travel-volume cities where Aedes aeygpti or albopictus are reported and where climatic conditions could be suitable for autochthonous transmission.
Conclusion: The rapidly evolving outbreak of chikungunya in the Caribbean poses a growing risk to countries and areas linked by air travel, including the United States where competent Aedes mosquitoes exist. The risk of chikungunya importation into the United States may be elevated following key travel periods in the spring, when large numbers of North American travelers typically vacation in the Caribbean.
Background: A novel coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causing severe, life-threatening respiratory disease has emerged in the Middle East at a time when two international mass gatherings in Saudi Arabia are imminent. While MERS-CoV has already spread to and within other countries, these mass gatherings could further amplify and/or accelerate its international dissemination, especially since the origins and geographic source of the virus remain poorly understood.
Methods: We analyzed 2012 worldwide flight itinerary data and historic Hajj pilgrim data to predict population movements out of Saudi Arabia and the broader Middle East to help cities and countries assess their potential for MERS-CoV importation. We compared the magnitude of travel to countries with their World Bank economic status and per capita healthcare expenditures as surrogate markers of their capacity for timely detection of imported MERS-CoV and their ability to mount an effective public health response.
Results: 16.8 million travelers flew on commercial flights out of Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates between June and November 2012, of which 51.6% were destined for India (16.3%), Egypt (10.4%), Pakistan (7.8%), the United Kingdom (4.3%), Kuwait (3.6%), Bangladesh (3.1%), Iran (3.1%) and Bahrain (2.9%). Among the 1.74 million foreign pilgrims who performed the Hajj last year, an estimated 65.1% originated from low and lower-middle income countries.
Conclusion: MERS-CoV is an emerging pathogen with pandemic potential with its apparent epicenter in Saudi Arabia, where millions of pilgrims will imminently congregate for two international mass gatherings. Understanding global population movements out of the Middle East through the end of this year’s Hajj could help direct anticipatory MERS-CoV surveillance and public health preparedness to mitigate its potential global health and economic impacts.
We present a framework for near real-time forecast of influenza epidemics using a simulation optimization approach. The method combines an individual-based model and a simple root finding optimization method for parameter estimation and forecasting. In this study, retrospective forecasts were generated for seasonal influenza epidemics using web-based estimates of influenza activity from Google Flu Trends for 2004-2005, 2007-2008 and 2012-2013 flu seasons. In some cases, the peak could be forecasted 5-6 weeks ahead. This study adds to existing resources for influenza forecasting and the proposed method can be used in conjunction with other approaches in an ensemble framework.