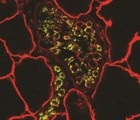
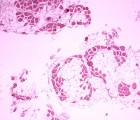
α dystroglycan (αDG) is part of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein (DAG) complex, a series of cytoskeletal, transmembrane, and membrane-associated proteins that serve to link the extracellular matrix (ECM) surrounding individual skeletal myofibers to the intracellular F-actin cytoskeleton. Glycosylation and ECM protein binding to αDG are regulated by a number of genes that, when defective, give rise to congenital or limb-girdle forms of muscular dystrophy termed dystroglycanopathies. One such dystroglycanopathy gene is LARGE. Here, we describe a method to produce and purify full-length, furin-resistant, recombinant αDG from CHO cells and CHO cells overexpressing LARGE (CHO-LARGE). In addition, we analyze the O- and N-linked monosaccharide composition of such proteins. αDG purified from CHO-LARGE cells had increased molar content of xylose and fucose relative to CHO, while no significant changes were found in N-linked monosaccharides. Glucuronic acid could not be quantified by the methods used. These studies describe a method to produce and purify the milligram amounts of αDG needed for certain biochemical methods, including monosaccharide analysis.
Key words: Dystroglycan, muscular dystrophy, xylose, fucose, laminin, LARGE
Correspondence: [email protected]