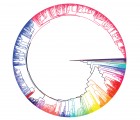
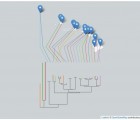
Quantifying the age of recent species divergence events can be challenging in the absence of calibration points within many groups. The katydid species Neoconocephalus lyristes provides the opportunity to calibrate a post-Pleistocene, taxa specific mutation rate using a known biogeographic event, the Mohawk-Hudson Divide. DNA was extracted from pinned museum specimens of N. lyristes from both Midwest and Atlantic populations and the mitochondrial gene COI sequenced using primers designed from extant specimens. Coalescent analyses using both strict and relaxed molecular clock models were performed in BEAST v1.8.2. The assumption of a strict molecular clock could not be rejected in favor of the relaxed clock model as the distribution of the standard deviation of the clock rate strongly abutted zero. The strict molecular clock model resulted in an intraspecific calculated mutation rate of 14.4-17.3 %/myr, a rate substantially higher than the common rates of sequence evolution observed for insect mitochondrial DNA sequences. The rate, however, aligns closely with mutation rates estimated from other taxa with similarly recent lineage divergence times.