Introduction: An outbreak of Lassa Fever (LF) reported and confirmed in Ondo state, Southwest Nigeria in January 2016 was investigated. This paper provides the epidemiology of the LF and lessons learnt from the investigation of the outbreak.
Methods: The incidence management system (IMS) model was used for the outbreak coordination. Cases and deaths were identified through the routine surveillance system using standard definitions for suspected and confirmed cases and deaths respectively. Blood specimens collected from suspect cases were sent for confirmation at a WHO accredited laboratory. Active case search was intensified, and identified contacts of confirmed cases were followed up for the maximum incubation period of the disease. Other public health responses included infection prevention and control, communication and advocacy as well as case management. Data collected were analysed using SPSS 20, by time, place and persons and important lessons drawn were discussed.
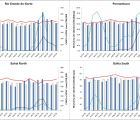
Results: We identified 90 suspected LF cases of which 19 were confirmed by the laboratory. More than half (52.6%) of the confirmed cases were females with majority (73.7%) in the age group ≥ 15 years. The Case Fatality Rate (CFR) of 63.2% among the laboratory-confirmed positive cases where 9 of 19 cases died, was significantly higher compared to the laboratory confirmed negative cases where 6 of the 65 cases died ( CFR; 8.5%) p ≤ 0.05. Two hundred and eighty-seven contacts of the confirmed cases were identified, out of which 267(93.0%) completed the follow-up without developing any symptoms and 2 (0.7%) developed symptoms consistent with LF and were confirmed by the laboratory. More than half of the contacts were females (64.5%) with most of them (89.2%) in the age group ≥ 25 years.
Discussion: One key lesson learnt from the investigation was that the confirmed cases were mainly primary cases; hence the needs to focus on measures of breaking the chain of transmission in the animal-man interphase during Lassa fever epidemic preparedness and response. In addition, the high case fatality rate despite early reporting and investigation suggested the need for a review of the case management policy and structure in the State. Key Words: Lassa fever, Outbreak Response, Incident Management System, Nigeria