Introduction: For effective public communication during major disease outbreaks like the 2014-2016 Ebola epidemic, health information needs of the population must be adequately assessed. Through content analysis of social media data, like tweets, public health information needs can be effectively assessed and in turn provide appropriate health information to address such needs. The aim of the current study was to assess health information needs about Ebola, at distinct epidemic time points, through longitudinal tracking.
Methods: Natural language processing was applied to explore public response to Ebola over time from July 2014 to March 2015. A total 155,647 tweets (unique 68,736, retweet 86,911) mentioning Ebola were analyzed and visualized with infographics.
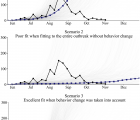
Results: Public fear, frustration, and health information seeking regarding Ebola-related global priorities were observed across time. Our longitudinal content analysis revealed that due to ongoing health information deficiencies, resulting in fear and frustration, social media was at times an impediment and not a vehicle to support health information needs.
Discussion: Content analysis of tweets effectively assessed Ebola information needs. Our study also demonstrates the use of Twitter as a method for capturing real-time data to assess ongoing information needs, fear, and frustration over time.